.
_________________ Alignment Projects _________________
Introduction
This task prepares existing translations for uploading to our translation memories. Then, they are reused in new projects. This process is called alignment.
Translation Memories, Segments and Alignment
What is a Translation Memory?
Translation memory or TM is a database of original source text and its respective translated segments. It works by automatically reusing any segments that are the same or similar on new projects.
- The more you translate, the more it grows, and the higher the chance is of translation memory matches.
- Translation memory is effective when source texts use identical or similar phrases.
- It’s also useful for updating documents or making small changes, since the majority of the translated text can be reused from the translation memory.
Segments and segmentation
In translation tools, segmentation involves dividing a source text into units for translation. These are called segments and they are a key component of alignment projects.
Depending on the configuration of the system, the source text is divided in different ways. Some of the most common options for segmentation are:
- Segments coincide with sentences and end in a full stop, a question or exclamation mark, a quotation mark, etc.
- A new segment is created after a paragraph break
- In bulleted lists (such as this one), individual segments are created for each item
When you work on an alignment project, keep this in mind and try to ensure segments match these characteristics.
What is document alignment?
A way to recycle translated material created outside of our translation tool. It requires the source and target versions of the documents to be aligned. The process creates a bilingual TMX file that feeds to a Translation Memory and is reused in new projects.
- The system takes two files, source and target, and segments them into translation units.
- Then, it attempts to match and connect the source and target units, with various degrees of success.
- After that, a translator goes through the alignment and makes the necessary adjustments to match source and target text correctly
- Finally, the Project Officer imports the resulting TMX into the translation memory.
Instructions
If there are any questions about the process, please do not hesitate to contact your Project Officer. They will help you out!
Request
You will be provided with:
- A spreadsheet with the pre-aligned source and target segments.
- The source and target files as reference material.
Process
Here is how you approach this task:
-
Familiarize yourself with the general structure and content of the source and target files. This helps you make informed decisions when aligning.
-
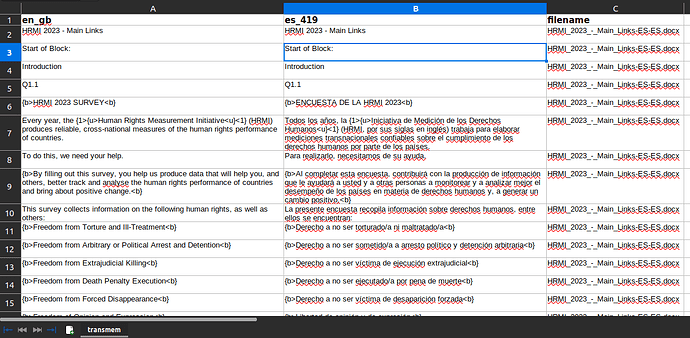
Open the project spreadsheet and take a look at the columns. It looks similar to the screenshot below.!
-
The file is simple and easy to use:
a. The original and translated segments are displayed on columns A and B, respectively.
b. Match the translations with the original segment by either:- Cutting and pasting the segments to position them next to each other.
- Deleting segments that do not have a match in the target language
-
Merging, Splitting, and Deleting: As seen earlier, segments can be created in different ways, and you may need to modify the segmentation by creating new segments or combining existing ones if the process did not work correctly. You can also delete a segment if you think it should not be part of the alignment.
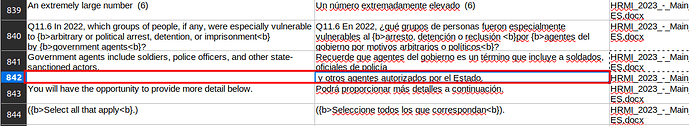
a. Merging: combine two segments in either source or target by copy-pasting them both into the same cells. Ex.: In the screenshot below, the target segment in row 842 needs to be combined with the one in row 841.
b. Splitting: divide a segment into two or more parts by moving the content into new cells.
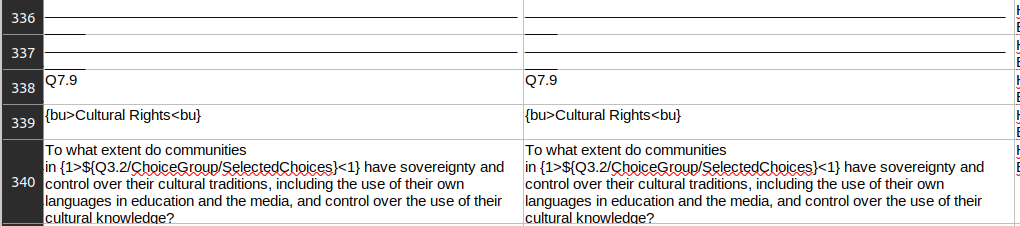
c. Deleting: select the segment you wish to remove and delete the content. Ex.: segments 336 and 337 below are just lines, and as such they should be deleted. Segment 339 is in English in the target, so it should be deleted as well.
-
Work your way through the document until you have aligned all units.
a. Spot checks: you may speed through large sections of the document which are properly aligned. In such cases, please:- Start from a pair of properly aligned segments.
- Scroll down approximately 30 segments and check if they continue to be properly aligned.
- If they do, repeat step 2. If they don’t, return to the segment in step 1.
- BE CAREFUL: the tool attempts to align segments automatically but it may fail. Be extremely careful when you proceed with spot checks.
b. Empty segments: if you are unable to find a match for a specific segment. The corresponding text may be:
- Within a neighbouring segment (you will need to use split or merge to correct this)
- Located in an earlier or subsequent section of the project. Look for the content in segments close by.
- Simply missing. In some rare cases, you may be unable to find the unit. After reviewing the document carefully, delete the unmatched unit.
-
Perform one final review of the document to ensure all segments have been covered and to go over the pre-delivery checklist.
-
Handover notes: you may have issues in the source file, problems you were unable to resolve, or areas in which you think improvements are needed. Submit them to the PO while you do the review. Otherwise, compile any pending points or comments in an email and share them with your PO.
Pre-delivery checklist
![]() Check that all source segments are aligned with the corresponding translated unit.
Check that all source segments are aligned with the corresponding translated unit.
![]() Verify that there are no miss-alignments by spot-checking the project every 30 segments.
Verify that there are no miss-alignments by spot-checking the project every 30 segments.